Agustín Delgado de Robles y Velasco
Madrid, 1923-2000
Agustín Delgado de Robles y Velasco began his studies at the Madrid School of Architecture in September 1943 and finished his degree in June 1951. He completed his doctorate and earned his PhD in Architecture on April 30, 1963.
When Delgado de Robles began his studies, Spain was rebuilding after the Civil War; as he finished his studies, new paths were beginning to emerge in Spanish architecture. It is worth highlighting certain architects from his year in both Madrid and Barcelona. Luis Cubillo, Arturo Guerrero, Luis Oriol and José Luis Romany, among others, graduated from the Madrid architecture school the same year he did. Notable students of the Catalan school include the teams of Bohigas-Martorell and Giráldez-López-Subías.
Delgado de Robles had always been interested in drawing and painting. He taught the course “Analysis of Forms” at the Madrid School of Architecture during the 1969-1970 academic year. In 1979, his oil paintings were exhibited in galleries in Madrid and Alicante.
From 1953 to 1956, he worked with Diego del Corral designing several residential buildings in Madrid. In 1956, he earned a position as a civil servant with the National Institute of Colonization (INC) at the delegation in Talavera de la Reina. He was later transferred to the Architecture Service in Madrid, led by José Tamés, a position he held until he requested leave in 1961.
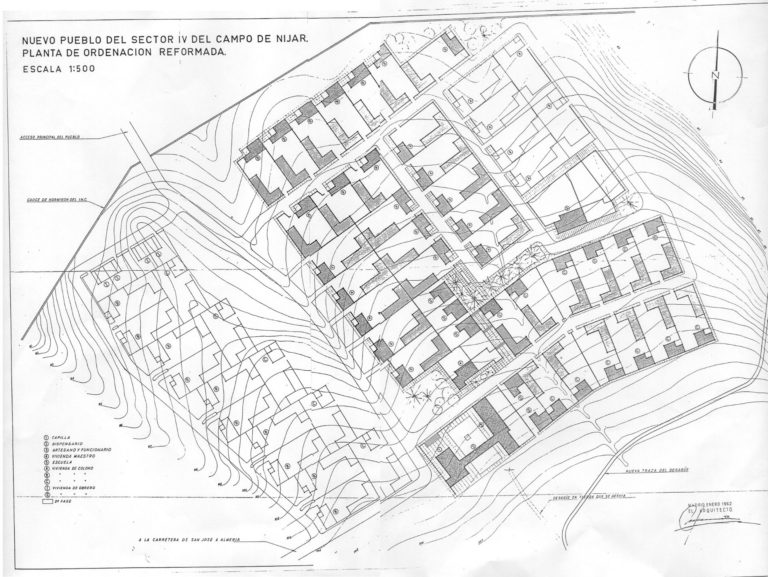
Over the course of those five years he designed eight towns in the southern half of Spain: the villages of Miramontes (1956) and Barquilla de Pinares (1957) in Caceres; Los Mirones (1958) in Ciudad Real; Atochares and San Isidro de Nijar in Almeria (1959); Puntalón in Granada (1960); Loriguilla in Valencia (1960); and Umbria de Fresneda in Ciudad Real (1961). In 1965, as an external collaborator with the Institute, a common practice for former government employees, he was commissioned to design the project for Pradochano in Cáceres.
He returned to the administration in 1981, at a time when the INC had become the Institute for Agrarian Reform and Development (IRYDA), where he stayed until his retirement on 1 December 1988 at the age of 65.
Delgado de Robles skirts tradition in various aspects and replaces the use of symmetry with repetition. He employs more abstract concepts for the façades of the houses in Loriguilla, Puntalón, San Isidro and Atochares. He shifts the openings towards the ends of the porches, creates small setbacks in the walls to generate shadow effects, both across a single floor and by grouping windows on different levels, and he uses the porches as a compositional element, sometimes on the ground floor as an entryway and other times on the upper floor as a sunroom.
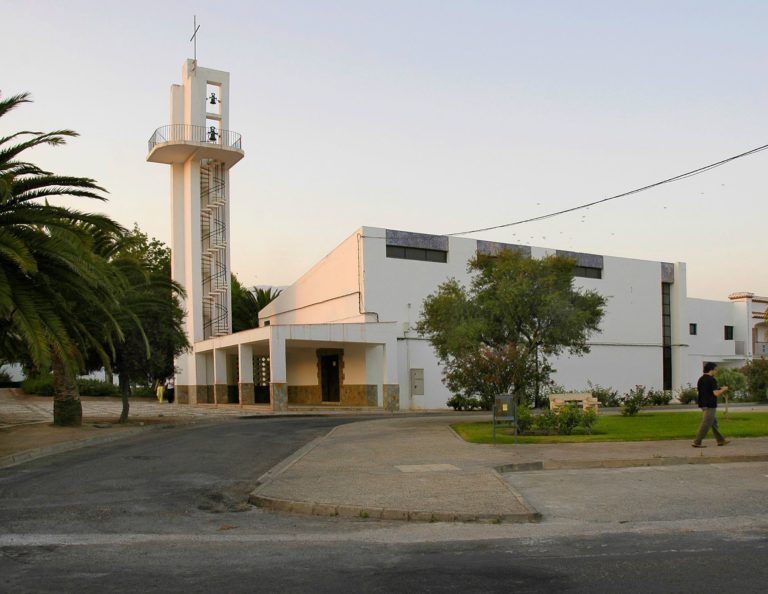
As for the roofs, there is a deviation from the usual sloped gabled shapes. In towns with small chapels like Umbría de Fresneda, Los Mirones, Barquilla de Pinares and Atochares, the solution is a slanted shed roof. Other times, in larger churches with bell towers, he uses innovative solutions, like in Pradochano, where an inclined plane connects the main nave with the slender tower, and the usual square footprint is replaced by a rectangular one.
Delgado de Robles also introduces modernity through the use of materials. One example of this is the use of mosaic tiles for the church in Puntalón or the mix of vertical spans of exposed brick and plastered brick in the aforementioned Pradochano church.
Agustín Delgado de Robles spent five years working with the Architecture Service at the INC and, although the period was short, his interesting contributions to the construction of new towns are unmistakable. Atochares is included in the Docomomo’s Registry of Housing, and a plaque was installed on the façade of the church in 2013 as a testament to the lasting interest of this Almerian town.
Biography by Miguel Centellas
Bibliography
- DELGADO ORUSCO, Eduardo, El agua educada. Imágenes del Archivo Fotográfico del INC. 1939-1973, Ministerio de Agricultura, Alimentación y Medio Ambiente (MAGRAMA), Madrid, 2015, DVD.
- RIVERO SERRANO, José, PERIS SÁNCHEZ, Diego (2014), El Instituto Nacional de Colonización en Ciudad Real, Diputación Provincial de Ciudad Real Ciudad Real, 2014.
- CENTELLAS SOLER, Miguel, JORDÁ SUCH, Carmen, LANDROVE, Susana, coords., La vivienda moderna. Registro Docomomo Ibérico 1925-1965, Barcelona, Fundación Caja de Arquitectos/Fundación Docomomo Ibérico, Barcelona, 2009.
- CENTELLAS SOLER, Miguel, RUIZ GARCÍA, Alfonso, GARCÍA-PELLICER LÓPEZ, Pablo, Los pueblos de colonización en Almería. Arquitectura y desarrollo para una nueva agricultura, Colegio Oficial de Arquitectos de Almería/Instituto de Estudios Almerienses/Fundación Cajamar, Almería, 2009.
- ALMARCHA NÚÑEZ-HERRADOR, Esther, Nueve pueblos de colonización en Ciudad Real, Diputación Provincial de Ciudad Real, Ciudad Real, 1996.